Loculated Pleural Effusion | Pleural effusions can be present in advanced stage malignancy such as lung, breast, and lymphoma to name a few. Pleural effusion is a rare complication and is generally similar to that seen in the rickettsial illnesses. (vats) with lysis of adhesions is also a viable option for loculated effusions. Encysted pleural fluid is visualized between the right upper and middle lobe (s). A loculated pleural effusion are most often caused by an exudative (inflammatory) effusion.
If the fluid cannot be drained, the lungs aren't able to expand and oxygenate the blood sufficiently. Pleural effusions are very common, and physicians of allspecialties encounter them. The lack of specificity is mainly due to the limitations of the imaging modality. A pleural effusion is due to the manifestations of another illness.; Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural space that is classified as transudate or exudate according to its composition and underlying pathophysiology.
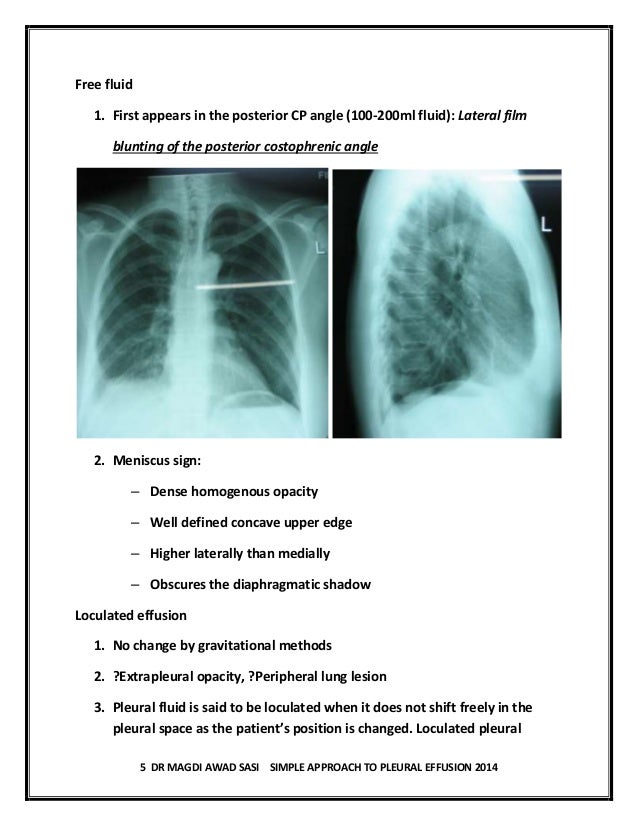
The reasons for effusion are many, and the specific diagnosis is often based upon tap or drainage of the fluid. Pleural effusion is a rare complication and is generally similar to that seen in the rickettsial illnesses. What are the different appearances of pleural effusion? Pleural effusions describe fluid between the two layer of tissue (pleura) that cover the lung and the lining of the chest wall. Surgical treatment of pleural effusion may include chest. But the doc still managed to find an 8cm pocket and removed 1600ml fluid. (vats) with lysis of adhesions is also a viable option for loculated effusions. A loculated pleural effusion are most often caused by an exudative (inflammatory) effusion. Encysted pleural fluid is visualized between the right upper and middle lobe (s). This type of effusion is empyema unless proven otherwise. Pleural fluid is seen extending to the right oblique fissure. Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural space that is classified as transudate or exudate according to its composition and underlying pathophysiology. Pleural effusions are very common, and physicians of allspecialties encounter them.
Normally, a small amount of fluid is present in the pleura. The doctor who performed the last one found my right pleural space was mostly filled with loculated effusion which is like clusters of small grapes and cannot be drained. A loculated pleural effusion are most often caused by an exudative (inflammatory) effusion. A pleural effusion occurs when fluid fills this gap and separates the lungs from the chest wall. Pleural effusions are very common, and physicians of allspecialties encounter them.

If it is clear that there are multiple loculations then it is wise to avoid delay and proceed directly to this procedure. Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. Most pleural effusions, whether free flowing or loculated, are hypoechoic with a sharp echogenic line that delineates the visceral pleura and lung. In general, pleural effusions can be divided into transudates (caused by fluid leaking from blood vessels) and exudates (where fluid leaks from inflammation of the pleura and lung). If the fluid cannot be drained, the lungs aren't able to expand and oxygenate the blood sufficiently. A pleural effusion is due to the manifestations of another illness.; We report a case in which loculated recurrent pleural effusion was treated by insertion of an indwelling tenckhoff catheter. Diffuse nodules and opacification in right lung with compressive atelectasis. The largest pocket of fluid is present posteriorly at the right lung base, with associated atelectasis and minor consolidation. The doctor who performed the last one found my right pleural space was mostly filled with loculated effusion which is like clusters of small grapes and cannot be drained. Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural inflammation, such as empyema, hemothorax, or tuberculosis. However, the most recent ultrasound has shown all my right pleural space is now filled with loculated. Empyema and large or loculated effusions need to be fo … at least 40% of all patients with pneumonia will have an associated pleural effusion, although a minority will require an intervention for a complicated parapneumonic effusion or empyema.
In general, pleural effusions can be divided into transudates (caused by fluid leaking from blood vessels) and exudates (where fluid leaks from inflammation of the pleura and lung). Medical dictionary for the health professions and nursing © farlex 2012 want to thank tfd for its existence? Normally, a small amount of fluid is present in the pleura. The lack of specificity is mainly due to the limitations of the imaging modality. Pleural effusions describe fluid between the two layer of tissue (pleura) that cover the lung and the lining of the chest wall.

In chf effusions are bilateral and more on right. Treatment may fail if the catheter is not placed optimally within the loculation or if the fluid is hemorrhagic or fibrinous. Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content. Pleural effusion that is confined to one or more fixed pockets in the pleural space. (vats) with lysis of adhesions is also a viable option for loculated effusions. If the fluid cannot be drained, the lungs aren't able to expand and oxygenate the blood sufficiently. Pleural fluid is seen extending to the right oblique fissure. Surgical treatment of pleural effusion may include chest. Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural inflammation, such as empyema, hemothorax, or tuberculosis. Icu patients cannot sit up and the effusion layers posteriorly. Malignant pleural effusion is a frequent complication of some common cancers. Causes of an exudative effusion are malignancy, infection, or inflammatory disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. A pleural effusion is due to the manifestations of another illness.;
Loculated Pleural Effusion: A pleural effusion occurs when fluid fills this gap and separates the lungs from the chest wall.
0 comments:
Post a Comment